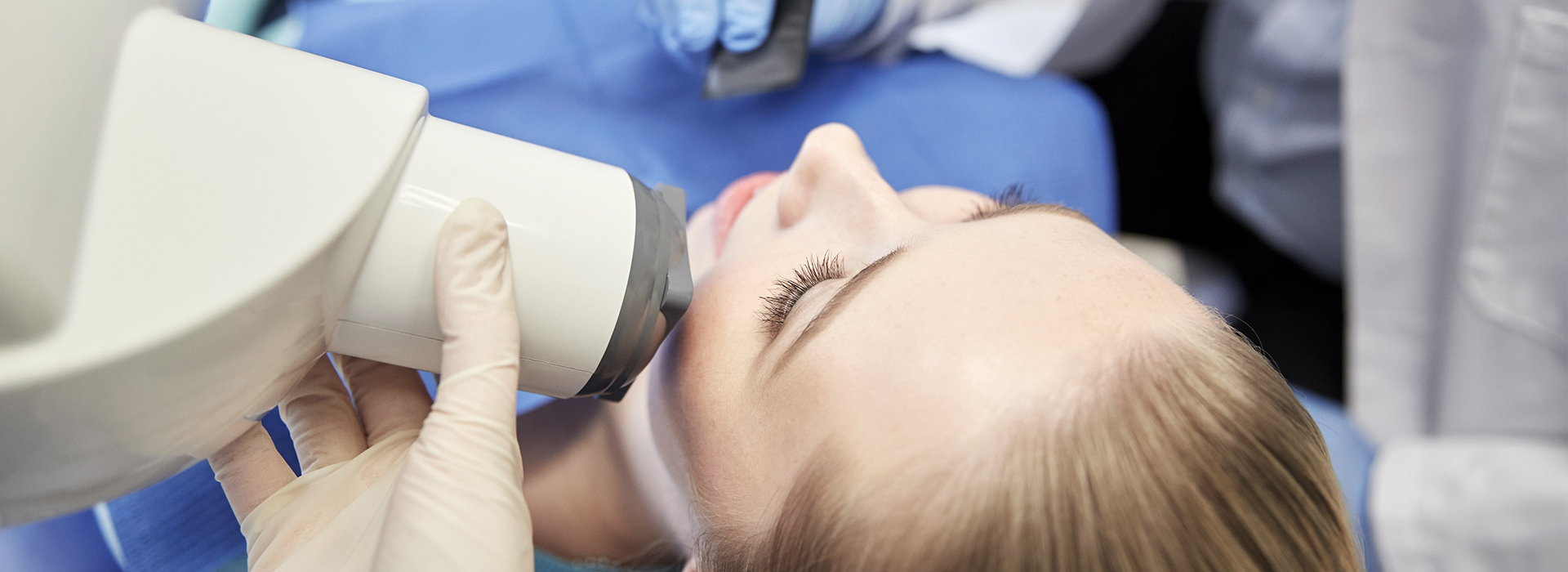
Digital radiography refers to dental X-ray systems that capture images with electronic sensors and specialized software rather than traditional photographic film. These images are immediately converted into digital files that can be displayed, enhanced, and stored on a computer. Because the full process happens electronically, clinicians can review high-resolution images almost instantly and make informed decisions without the wait associated with film processing.
At its core, digital radiography preserves the same clinical goals as conventional X-rays: to reveal tooth structure, root anatomy, bone levels, and other conditions that are not visible during a visual exam. What changes is the method of capture and the range of tools available for viewing and analyzing the data. Advanced software allows for contrast adjustment, zooming, and measurements that enhance diagnostic clarity while keeping the workflow efficient.
Unlike more technical descriptions that can overwhelm patients, it helps to think of digital radiography as a modern camera for your mouth—one that produces clear, editable images that support faster diagnoses and better treatment planning. This capability makes it an important part of contemporary dental care and routine preventive exams alike.
Vaccaro Aesthetic and Family Dentistry uses digital imaging as part of a broader commitment to modern, patient-centered dental care. By integrating digital X-rays into regular checkups and more advanced evaluations, the practice is able to provide precise, evidence-based guidance while keeping patient comfort and safety in focus.
One of the most notable advantages of digital radiography is its ability to reduce radiation exposure compared with older film-based techniques. Although any necessary X-ray involves only a small amount of radiation, digital sensors are more sensitive to X-ray photons, which means diagnostic-quality images can be produced with lower doses. This improves safety without compromising image clarity.
Beyond safety, the image quality from digital sensors often surpasses that of film. Digital images have greater dynamic range and contrast, which helps clinicians detect early signs of decay, subtle fractures, and changes in bone density. Software tools can highlight areas of concern, allowing the dental team to identify issues sooner and with greater confidence.
Because digital images are captured electronically, they are less susceptible to the artifacts and inconsistencies that sometimes occur with film processing. That reliability contributes to more consistent records over time, which is especially useful when monitoring the progression of conditions such as periodontal disease or evaluating the success of restorative treatments.
Collectively, these improvements in safety and diagnostic accuracy support more conservative, targeted care. When clinicians can see more clearly, patients benefit from treatments that address the actual problem rather than relying on broader or more invasive approaches.
Digital radiography dramatically speeds up the clinical workflow. Once an X-ray is taken, the image appears on a computer screen within seconds, ready for review. This immediacy shortens appointments, reduces the need for repeat visits, and allows dentists to discuss findings with patients during the same appointment—supporting clearer communication and more efficient decision-making.
Another practical advantage is the ease of sharing digital files with specialists, laboratories, or referring providers. When a case requires input from an oral surgeon, endodontist, or orthodontist, high-quality images can be transmitted electronically and securely. That capability shortens treatment timelines and improves coordination for multidisciplinary care.
Digital storage also simplifies long-term record keeping. Images are indexed within the patient’s electronic chart, which makes retrieval quick and reduces the physical storage burden of film archives. This organization helps the dental team track changes over time and compare current images with past records to evaluate treatment outcomes.
Ultimately, the streamlined workflow and collaborative possibilities of digital radiography lead to more integrated care. Patients experience a smoother, more informative visit, and clinicians have the tools they need to work efficiently and accurately across the full spectrum of dental services.
Having a digital dental X-ray is a straightforward and quick process. During a routine exam, a small sensor is positioned in the mouth where the tooth or area of interest needs to be captured. The sensor is connected to the computer, and when the X-ray is taken, the exposure lasts only a fraction of a second. Because the sensor is often smaller and more flexible than traditional film holders, many patients find the experience more comfortable.
After the image is captured, the clinician will immediately view it on a monitor. This allows for an on-the-spot explanation of any findings and enables the team to show patients the exact areas of concern. Visual aids like zoom, brightness adjustment, and side-by-side comparisons help make complex information more understandable and directly relate images to recommended care.
If additional views are needed, the process is repeated quickly and safely. Protective measures such as lead aprons or thyroid collars may still be used according to best-practice guidelines and patient needs. The overall time added to an appointment is typically minimal, but the diagnostic value gained is significant.
Because images are digital, patients can also request copies for their personal records or to share with another provider. The practice will follow privacy and security best practices when handling and transferring any medical images to ensure confidentiality and compliance with record-keeping standards.
Digital radiography supports both immediate diagnosis and long-term oral health management. Clear, consistent imaging allows clinicians to create precise treatment plans—whether restoring a tooth, placing an implant, or monitoring periodontal status. The ability to measure and document anatomical features helps ensure predictable outcomes and informs follow-up care.
For ongoing monitoring, digital images provide an easy way to compare current and past studies. Subtle changes in tooth structure, bone levels, or root health become easier to detect when high-quality images are available side-by-side. Early detection through imaging often opens the door to less invasive interventions and improved preservation of natural teeth.
Digital records also facilitate patient education and engagement. When patients can see clear images of their own mouths and review them with the dental team, they are better positioned to understand treatment options and to participate in preventive strategies. This informed partnership supports healthier outcomes and greater satisfaction with care.
As imaging technology continues to evolve, its role in preventive dentistry and precise restorative treatment will only grow. Practices that embrace digital radiography position themselves to deliver care that is safer, more predictable, and more focused on long-term oral health.
In summary, digital radiography is a cornerstone of modern dental diagnostics—combining safety, clarity, and efficiency to improve patient care. If you have questions about how digital imaging is used in our office or whether it’s appropriate for your dental needs, please contact us for more information.

Digital radiography is a dental imaging method that uses electronic sensors and computer software to capture and display X-ray images instead of traditional film. The sensor converts X-ray photons into a digital file that appears on a monitor within seconds, allowing immediate review and adjustment. This technology supports high-resolution images that can be enhanced, measured, and stored electronically for clinical use.
Because images are digital, clinicians can zoom, adjust contrast, and compare views side-by-side to improve diagnostic clarity. The workflow is faster and more efficient than film processing, which helps shorten appointments and reduce repeat exposures. Digital radiography is commonly used in routine exams as well as for more detailed evaluations when planning restorative or surgical care.
Unlike traditional film, digital radiography relies on sensors that are more sensitive to X-rays and produce an immediate electronic image rather than requiring chemical development. The increased sensitivity often allows for lower radiation doses while maintaining or improving image quality compared with film. Digital images also avoid many of the artifacts and inconsistencies associated with film processing.
Another major difference is the ability to manipulate images after capture: clinicians can enhance brightness, contrast, and magnification to reveal subtle findings. Electronic storage eliminates the need for physical film archives and makes retrieval and long-term comparisons easier. Overall, the transition to digital improves diagnostic reliability and clinical efficiency.
Digital radiography is considered safe and routinely used in modern dental practice because sensors require less radiation to produce diagnostic-quality images. The actual dose from a dental X-ray is very small, and the increased sensitivity of digital detectors helps minimize exposure while still delivering clear images. Protective measures such as lead aprons or thyroid collars may be used based on best-practice guidelines and individual needs.
Certain groups, such as pregnant patients, should always inform the dental team so that exposure can be minimized or deferred when appropriate. Clinicians follow established safety protocols and equipment standards to ensure exposures are kept as low as reasonably achievable. If you have specific health concerns, discuss them with your dental team so they can tailor imaging decisions to your situation.
Digital radiography reveals internal and sub-surface conditions that are not visible during a standard visual exam, including early tooth decay between teeth, the extent of root fractures, and changes in bone level associated with periodontal disease. It also helps identify abscesses, cysts, and other pathologies that may be developing below the gumline. These findings are critical for diagnosing problems early, when less invasive treatment is often possible.
High-resolution images and software tools support precise measurements of tooth and bone anatomy, which improves the accuracy of diagnoses and treatment planning. Side-by-side comparisons with prior images make it easier to detect subtle changes over time. Early detection through imaging can preserve tooth structure and guide targeted, conservative care.
In most cases there is no special preparation required for a digital dental X-ray; normal eating and medication routines can usually continue as normal. You may be asked to remove jewelry, removable dental appliances, or anything that could interfere with the imaging process. If you are pregnant or suspect you may be, inform the dental team so they can take extra precautions or defer imaging when appropriate.
For children or patients with a strong gag reflex, the team may use specialized positioning or sensors to improve comfort and image capture. Bringing previous dental images from another provider can be helpful but is not always necessary. If you have concerns about comfort or anxiety, let the staff know so they can accommodate you during the appointment.
Capturing a digital dental X-ray is typically very quick; each exposure lasts only a fraction of a second and the resulting image appears on the computer almost immediately. The overall time added to a routine exam is usually minimal, though more comprehensive imaging sessions may take longer depending on the number of views needed. Because images are available instantly, clinicians can review them with patients during the same visit.
After the image is captured, the dentist or hygienist will examine it, adjust display settings if needed, and explain any findings using magnification or annotations when helpful. Images are entered into the patient’s electronic chart for future reference and monitoring. Patients may request copies of their images for personal records or to share with another provider, and the practice will follow privacy and security practices when transferring files.
Digital images are an essential tool for precise treatment planning, allowing clinicians to measure anatomical structures, assess tooth and root relationships, and evaluate bone levels for restorative and surgical procedures. These objective data inform decisions about fillings, crowns, implant placement, and endodontic care, helping clinicians tailor interventions to each patient’s anatomy. The ability to annotate and measure images improves communication within the dental team and with specialists.
At Vaccaro Aesthetic and Family Dentistry, digital radiography is integrated with electronic records to track changes over time and document treatment outcomes. Comparing current images with previous studies makes it easier to detect gradual changes that warrant intervention or continued observation. This longitudinal view supports preventive strategies and helps clinicians provide more predictable, conservative care.
Yes, one of the practical advantages of digital imaging is the ability to transmit high-quality images electronically to specialists, laboratories, or referring providers. Secure, HIPAA-compliant methods are used to send files so that clinical teams can collaborate efficiently and expedite coordinated care. Electronic sharing reduces delays that earlier film-based systems could introduce and helps ensure that all providers have access to the same diagnostic information.
Before transferring images, practices typically obtain patient consent and follow privacy and record-retention protocols. Digital exchange supports faster decision-making for cases that require multidisciplinary planning, such as implant placement or complex restorative work. Patients benefit from smoother coordination and shorter treatment timelines when information flows securely between providers.
Digital X-rays are stored in the patient’s electronic health record and are typically backed up on secure servers to protect against data loss. Images are indexed so they can be retrieved quickly for comparison and follow-up care, eliminating the need for physical film storage. Regular backups and redundant storage systems help preserve clinical records over the long term.
Access to digital images is controlled through user authentication, role-based permissions, and other security measures that restrict who can view or modify records. Practices follow applicable privacy regulations and industry best practices to safeguard patient information. If you have questions about how your records are handled, the dental team can explain their specific security and privacy procedures.
Yes, digital dental imaging includes several modalities that serve different diagnostic purposes: intraoral sensors for bitewing and periapical views, panoramic radiography for a broad overview of the jaws, and three-dimensional cone beam CT (CBCT) for detailed volumetric analysis. Intraoral sensors are the most common for routine decay detection and root evaluations, while panoramic images are useful for assessing overall jaw relationships and eruption patterns. CBCT is reserved for cases that require precise 3-D information, such as implant planning or complex surgical assessments.
The selection of modality depends on the clinical question, the level of detail required, and the patient’s individual needs. Dentists will recommend the most appropriate type of imaging to answer a diagnostic or treatment-planning question while keeping radiation exposure as low as reasonably achievable. Using the right modality for the situation ensures accurate information and more predictable outcomes.

Ready to book your next dental visit or learn more about our services?
Getting in touch with Vaccaro Aesthetic and Family Dentistry is quick and easy. Our friendly team is here to help with scheduling, answering questions about treatments, and addressing any concerns. Whether by phone or our convenient online form, we make connecting with us easy. Take the first step toward a healthier, more confident smile—contact us today and experience personalized dental care that truly makes a difference.